SEO Tags: 8 Tags Critical for Rankings and Traffic
I imagine that SEO must seem like a really weird digital marketing channel at first.
Well, you can’t dispute its effectiveness, of course. But doesn’t it seem a little strange that so much of your success with driving organic traffic relies on optimizing things that no one ever sees?
Take SEO tags, for example. Users never see many of them. Yet, it’s hard to imagine that a page could rank well in the search results without well-optimized image tags, the canonical tag, and more.
Ignoring or under-utilizing meta tags is one of the most common issues that prevent companies from achieving high rankings and traffic.
In this guide, I will show you how to avoid it for your brand. What’s more, you’ll learn everything you need to know to optimize all of the critical SEO tags on your website.
So, let’s begin.
Why Are Tags So Important to SEO?
Most SEO tags are completely invisible to your visitors. Unless someone actively opens up a page’s code, they’ll never see the canonical tag, the image alt text, or the schema markup.
That’s because those tags are not there for them.
You optimize them to give additional information and directives to search engines. Every time a search engine crawler visits a page, it scans the code and collects information about its topic and the context behind it, its target language, and so on.
Much of that information comes from SEO tags.
Here’s what role tags play in optimizing a page:
- Tags communicate the topic of the page to search engines. Properly optimized meta title and meta description tags or header tags help search engines better understand what the page is about.
- Meta tags and header tags also ensure that search engines know what keywords and queries to rank the page for. Those tags bring clarity about the page’s relevance to user’s search queries.
- Tags can also tell search engines how to read a page. The Schema markup (we’ll be talking about it in more depth shortly) explains what different elements on a page mean and what content they include. Such information helps Google to evaluate better and make sense of what’s on the page.
- Some tags tell search engines who should see the page. For example, the Hreflang tag outlines to what language or country the page is the most relevant.
- Other tags clarify the page’s place in the site’s hierarchy. They can prevent duplicate content or keyword cannibalization issues, and more.
- Tags can even give search engines directions to follow.
In short, SEO tags provide context for many aspects of the process of indexing and ranking a page.
Without SEO tags, you leave your rankings to chance. Sure, Google might realize the page’s topic without relevant tags. It might know what queries to rank the page for too.
On the other hand, having properly-optimized tags increases your chances for all that happening. And that’s purely because you leave nothing to chance.
With that out of the way, let’s see which meta tags are critical for driving organic traffic and how to optimize them for SEO success.
8 Most Important Tags for SEO
#1. Title Tag
The title tag is a short HTML snippet appearing in the <head> section of the page’s code. This means that it does not display on the actual page. As a visitor, you can see it in two places:
First, the title tag appears as the clickable headline of a search listing. It’s that big blue link you see when searching and the one you click to access the content.
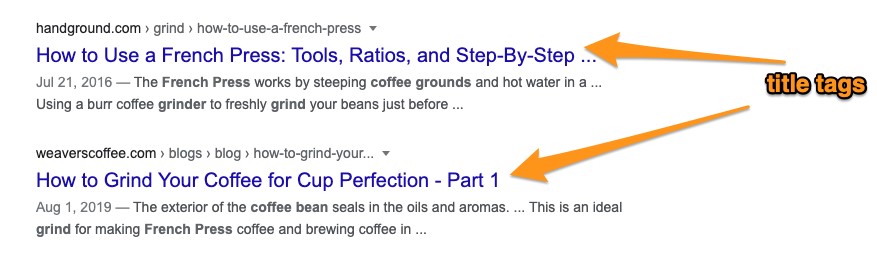
You can also see it in the title of a browser’s tab. The title of the tab comes directly from the SEO title tag.
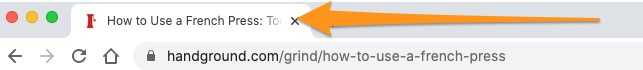
But of course, it’s importance goes far beyond displaying the title of the page.
- Search engine crawlers review the title tag and use its content to determine the page’s topic. As a result, the more relevant the tag is to the page’s content, the easier it will be for the search engine to rank it for relevant keywords.
- Typically, the title tag is also the very first thing users see in the search results. Therefore, its relevance to their search intent will affect their decision whether to click on a listing or not. That, in turn, directly affects a page’s organic CTR and performance.
Best Practices for Optimizing the Title Tag:
- Create unique title tags for each page on the site. Even if a page isn’t essential for your SEO strategy, give it a unique title. This will help the search engine to understand all your content
- Write no longer title tag than 5-60 characters to display in the search listing in full.
- Include the page’s target keyword (or its variation – more on this next) in the title tag. Ideally, place it as early in the tag as possible.
- Write the title tag for visitors to engage them with your search listing. This may require you to include a keyword variation rather than the exact search phrase you want the page to rank. There is no problem in doing so as Google and other search engines can determine your title tag’s meaning and still rank the content for relevant keywords.
- If you run a local business, include your location in the title as well. It will help the search engine determine where to rank you in the local search.
#2. Meta Description Tag
The meta description tag also renders in the <head> section of the page’s HTML code, meaning that its content is not visible on the page.
It’s also not a ranking factor. Google does not use it to determine how to rank a page in the search results.
However, the tag assists your SEO efforts in other ways.
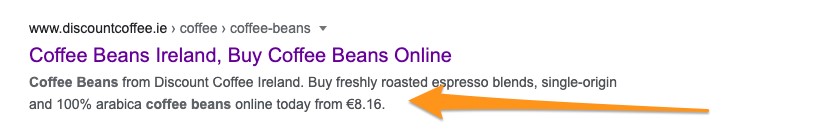
First, it often forms a part of your organic search listing.
Historically, Google would use the meta description tag to display in the SERP snippet, under the clickable headline.
That’s what’s happening for this page, for example.
These days, however, Google often uses a snippet of the page’s content if it finds it more relevant to the searcher’s query and the intent.
Take a look at this search result, for example.
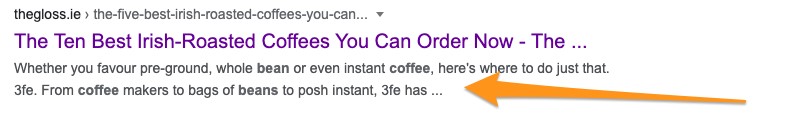
The actual meta description is different from what the company specified in the HTML code.

Second, the description affects your organic click-through rate. Since the description is the largest part of the search snippet, it provides searchers with additional information about your content and helps them determine whether to click on it or not.
What’s more, if the description contains words relevant to the person’s search query, those phrases will appear in bold to communicate their relevance to the object of the search.
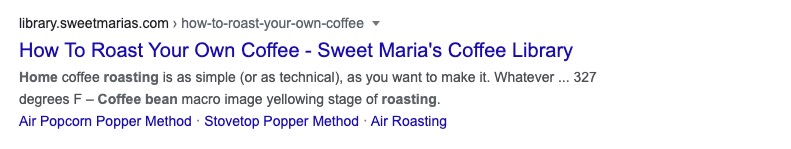
(An example of Google setting phrases from the search query in bold. Query: “Home roasting coffee beans”)
Best Practices for Optimizing the Meta Description Tag:
- Give each page a unique meta description, and ensure that it communicates the topic of the page.
- Your meta description should be no longer than 160 characters.
- Include keywords and phrases that reflect the topic of the page. You don’t have to include all the keywords but make sure that you include the most important phrases related to your page’s topic.
- Use active language to entice someone to click on your listing (i.e., use words like discover, learn, etc.)
#3. Heading Tags
Heading tags (i.e., H1, H2, H3, etc.) are part of almost every written content, online or off.
They act as subheadings in the content, helping to bring structure and organization to the text.
This very guide is split into separate sections with heading tags. It’s thanks to them that you know what each part of the copy is about.
That’s how they assist your SEO efforts too.
First things first, heading tags are not considered ranking factors. Although including a keyword in them is considered a good practice, Google regularly states that it does not look at heading tags when determining how to rank a web page.
Yet, without headings, search engines would, most likely, find it more difficult to crawl and index content.
Similarly, headings provide a much better user experience. It’s easier for a person to read and enjoy a well-organized piece of content. What that, the chances of them staying longer on a page increase, improving the page’s SEO engagement metrics.
Best Practices for Using Heading Tags:
- Use no more than a single H1 tag per page. Typically, this is your page’s title. If possible, include the target keyword or its variation in this heading.
- Make sure that headings are relevant to the section of the content they describe.
- Nest headings in order, H1 -> H2 -> H3, etc.
#4. Image ALT Tags
The image’s ALT tag is a short snippet of text added to the HTML code for an image to describe its contents. And that’s where its importance for SEO lies.
Search engines can’t “see” images on a page, of course. To them, each image is described by the code used to place it. And so, the more information about an image that code includes, the better search engines can understand an image.
But why is it important for them to do so in the first place?
Well, there are several reasons.
First, because images can also communicate topical relevancy to Google, in most cases, images on a page somewhat reflect its topic, after all. So, the better Google can understand those images, the clearer it might be about the page’s topic.
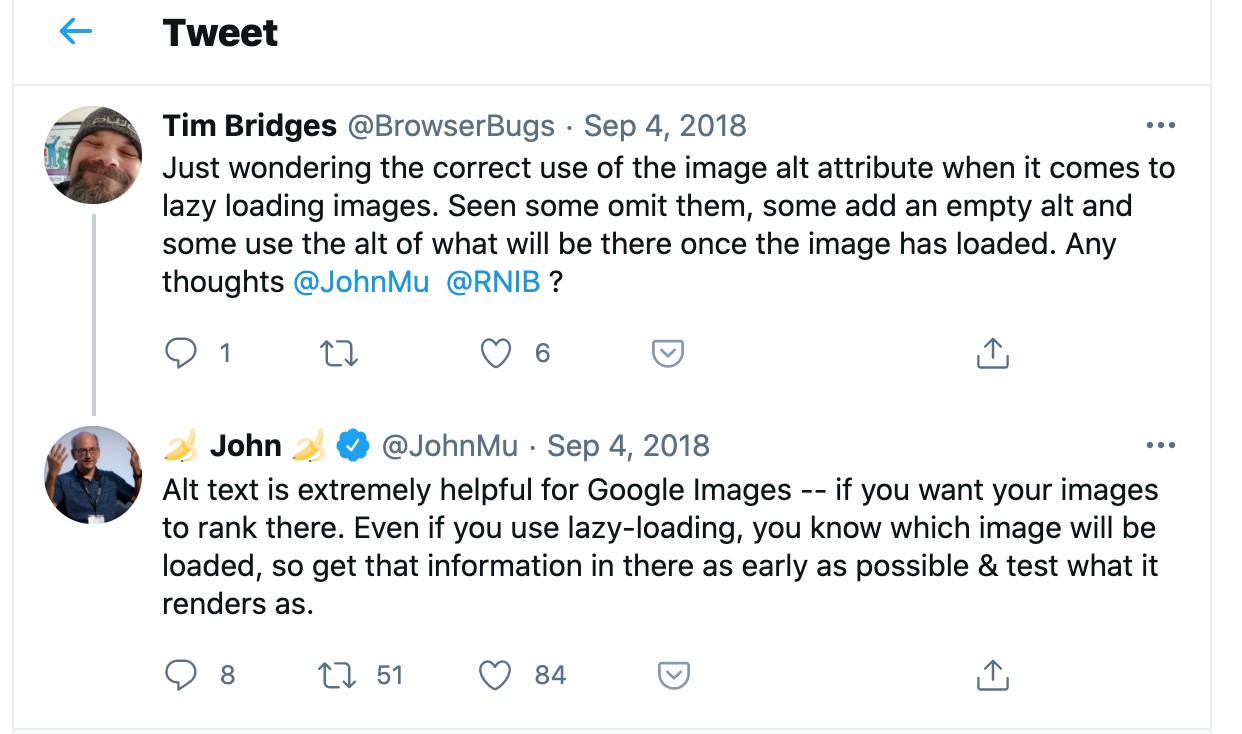
Also, properly optimized alt tags help rank in Google Images. Here’s a brief statement from Google’s John Mueller on that matter:
Best Practices for Optimizing Image Alt Tags:
- Define the ALT tag for the most important images on the page, at least. Ideally, optimize the tag for every image on the page.
- Make the tag’s copy descriptive, and don’t stuff it with keywords. Since images, most likely, relate to the page’s content, describing them will provide additional context to the search engines to better understand the page’s topic.
#5. Robots Tag
The robots tag does just one hugely significant thing on a page. It tells search engine crawlers how to crawl and index a page’s content.
You can tell a search engine not to include a particular page in its index with the robots tag. You can also instruct it to follow all links on that page, regardless of not indexing it. You can give crawlers other directives and ask them not to index images on a page.
Overall, the robots tag allows you to communicate what you’d like a crawler to do when it accesses the page.
Worth noting: The robots tag gives directions to search crawlers. Crawlers, however, do not have to follow those.
Best Practices for Using the Robots Tag:
- Use the tag when necessary, and always double-check the directives you’re giving. It’s easy to overlook something and prevent crawlers from indexing the most important content, for example.
- Use the tag on any pages that do not carry any significance for SEO or do not want to appear in the SERPs.
#6. The Canonical Tag
Often, the same page might have different unique URLs pointing to it.
This often happens when the website adds dynamic session variables is the original URL, perhaps due to a user triggering filters on a page.
Even though the person sees the same page, its URL has been altered to accommodate dynamic variables. As a result, the URL will look unique to the search engine, and it might consider the page unique as well.
Such a situation may confuse the search engine. It might simply not know which URL to rank for the target phrase. It might also begin considering all those pages as duplicates and penalize you for having duplicate content.
The canonical tag solves all these problems and more. It tells the search engine which URL to consider as original to include in the search results.
Best Practices for Using the Canonical Tag:
Use the canonical tag on every page. On most pages, it will be self-referencing (meaning that the tag will reference the same URL it is placed on.) However, at times, it may also help you mark:
- Pages with similar content,
- Duplicate, dynamically-created versions of the same page with unique URLs.
#7. Hreflang Tag
If your website targets audiences worldwide, the hreflang tag will allow you to ensure that they always see the most relevant page.
That’s because the hreflang tag tells search engines which language and country to display a specific page.
The tag resides in your page’s code and defines both the language and the territory a page targets.
The hreflang tag looks like this:
<link rel=”alternate” href=”http://domain.com” hreflang=”en-us” />
For example, if your company offers content in both Spanish and English, with the hreflang tag, you can tell Google when to display content in each language. As a result, your Spanish-speaking visitors would see the content in that language, for example.
The same goes for price currency. Thanks to the hreflang tag, online stores can display prices in USD to U.S. customers, but use EURO for visitors accessing their stores from the European Union, and so on.
As a result, the hreflang tag allows you to provide a much better user experience and target the content more precisely for relevant languages and territories.
The tag also eliminates the duplicate content issue from having pages with the same content in different languages. With a properly optimized hreflang tag, Google and other search engines will know that these pages are intended for different users.
Best Practices for Using the Hreflang Tag:
- Hreflang tag is only required for pages that target different and specific audiences (by location or language).
- When setting up the tag, make sure that you specify both language and country in the right order.
#8. The Schema Markup
The Schema markup consists of many different tags. All of them serve the same purpose, though – They allow you to organize better and define information on a webpage. The schema also helps search engines recognize different elements on a page and understand their meanings. With Schema, you can tell a search engine which part of the page contains the logo, or the company’s address, or your ratings and reviews, and more.
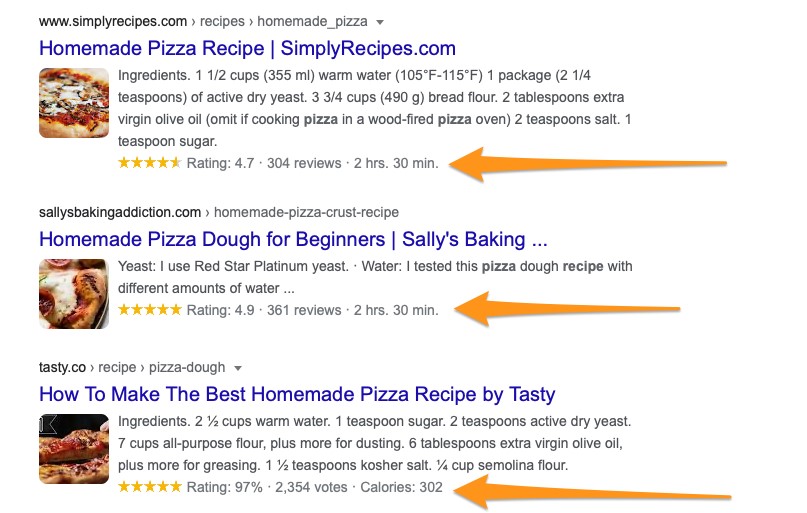
The search engine, in turn, can use this information to provide additional information to web users in the search listings. Here are a couple of examples.
Listings for those recipes include additional information (ratings, no. of reviews, and preparation time.) All of this info comes directly from the content marked with relevant Schema tags.
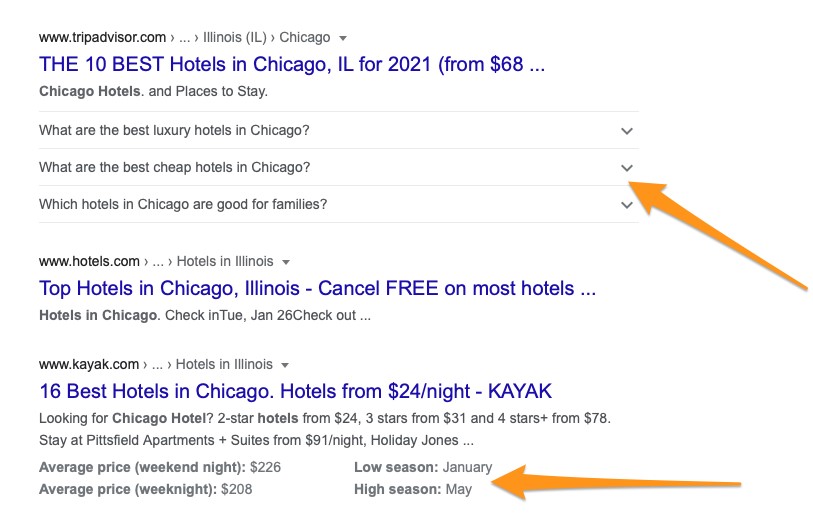
Users searching for hotels might often see pricing and availability, as well as additional FAQs regarding the target destination in the search listing. All that data comes from content marked with relevant Schema markup as well.
In both examples, and many other use cases for Schema, the markup helps search engines understand what specific words or data on a page means.
That’s also why you should use Schema tags when optimizing web pages. By doing so, you give search engines information with which they can enrich your SERP listing. That information, in turn, helps make your listing more visible and contribute to a higher organic click-through rate.
Best Practices for Using the Schema Markup:
- Schema is a vast and complex markup, with different tags and even tag categories relating to businesses, events, and other types of information. My best advice would be to review Schema documentation carefully to identify Schema’s type related to your business or content.
- Test the markup thoroughly before pushing live. Errors in the markup may result in search engines failing to understand the information or your pages becoming uncrawlable by their crawlers.
And There You Have It…
You now know the eight of the most essential SEO tags affect rankings, traffic, and revenue from the organic search.
Use them, and use them well. Although they might seem like insignificant snippets of code, most of those tags carry enormous SEO weight. Believe me when I say that they can truly make or break your content’s performance.
Hopefully, with this guide, you also know exactly what tags to focus on and how to use them to boost your SEO efforts.
Good luck!
Located At
2121 W Spring Creek Pkwy
Plano, TX 75023
Start Your Free Website Audit
© 2025 Envoca - Digital Marketing & Local SEO Agency. All Rights Reserved